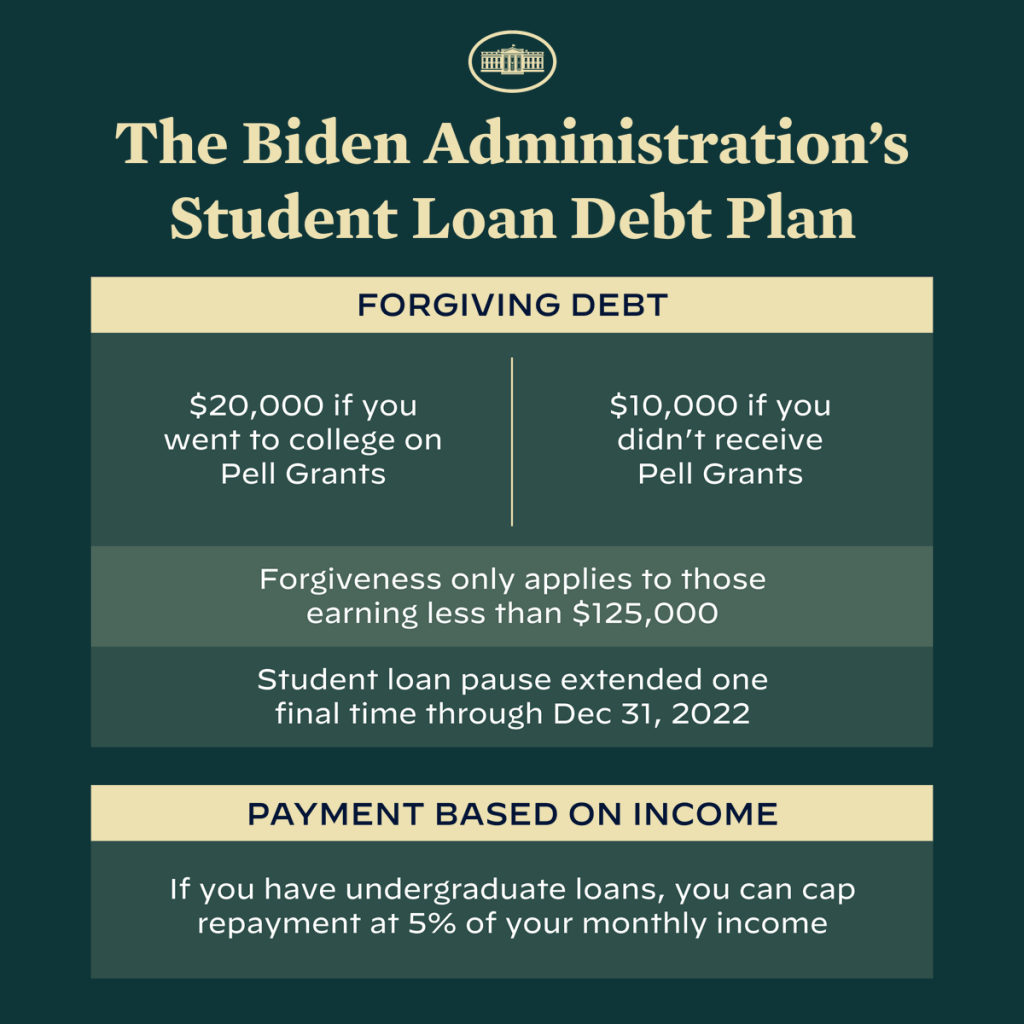
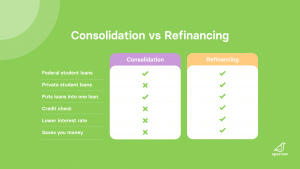
A great way to reduce your student loan debt is to refinance. An important part of that is looking for a good lender that will offer you good terms. In fact, the best refinance companies are going to give you the best terms. But, what do you even look for? And where do you start?
What to Look for in a Student Loan Refinancing Company
The purpose of refinancing your student loan(s) is to secure a better interest rate or terms.
So, when looking for a student loan refinancing company, you first want to look at their terms and policies. This includes their requirements for approval, the loan terms, cosigner policies, and fees. Here’s a couple things to consider:
- Is the interest rate on the loan lower than what you currently have?
- Does the lender offer more favorable terms (ie. a longer repayment period) than what you currently have?
Additionally, find out what kind of benefits they offer if any. Do they offer help in the event of financial hardship like the loss of a job? This includes things like forbearance and deferment options.
Make sure the new loan you select offers you a better interest rate or more favorable terms than what you currently have. If it does neither, then refinancing is not an advantageous decision.
Best Student Loan Refinancing Companies
To help you in your search, we’ve made a list of the best student loan refinancing companies.
Arkansas Student Loan Authority (ASLA)
The Arkansas Student Loan Authority offers loans to Arkansas residents or students who have attended a school in the state. They offer competitive rates and flexible terms to those who qualify. ASLA is best if you either live in or attended school in Arkansas and want competitive interest rates and flexible loan terms.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Competitive interest rates • Ability to refinance several types of loans • Variety of repayment options • Cosigner release option after 48 months • Offers 0.25% interest rate reduction for opting into auto-debit payments |
• Strict residency requirements • Inaccessible for international students |
Brazos is a nonprofit lender that provides student loan refinancing to Texas residents. Students must have at least an undergraduate degree in order to take out a refinance loan with them. Brazos offers competitive interest rates and flexible terms to those who qualify. Brazos is best if you are a Texas resident and have at least an undergraduate degree, though the degree does not have to be from a Texas school.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Work with a nonprofit, rather than a traditional lender • Competitive interest rates • Variety of repayment terms ranging from 5 to 20 years • Generous forbearance options |
• Strict eligibility criteria • No cosigner release • No bi-weekly payment via autopay • Students cannot take over parent PLUS loans that parents took out on their behalf |
College Ave offers student loan refinancing and is known for their strong customer service, competitive interest rates, and flexible loan terms. For example, College Ave offers nonstandard 6- or 9-year loans, which is unlike many other private lenders. College Ave is best if you want access to good customer service and a flexible repayment term that better matches your budget.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Strong customer experience • Competitive rates • Choose any loan term between 5 and 15 years including nonstandard terms such as 6 or 9 years |
• Limited eligibility criteria • Unclear forbearance policy • Not available to borrowers without a degree, visa holders, or those with parent PLUS loans • Doesn’t allow spousal consolidation loans |
Earnest offers student loan refinancing with customizable repayment plans where you can choose your repayment term down to the month. Earnest also has forward-looking eligibility criteria and offers competitive interest rates. Earnest is best if you don’t have a cosigner and want a repayment plan customized to your situation.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Competitive interest rates • Customizable payments and loan terms • Option to skip one monthly payment every year • Allows biweekly payments via autopay |
• Refinancing is unavailable in Kentucky and Nevada • Variable interest rates aren’t available for borrowers in all states • You can’t apply with a cosigner • Student borrowers cannot take over parent PLUS loans that parents took out on their behalf |
INvestED offers student loan refinancing to Indiana residents and students who attended school in Indiana. They offer a variety of repayment options, competitive interest rates, and flexible terms. INvestED is best if you are an Indiana resident or attended school in Indiana and want access to different repayment options.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Competitive interest rates • You can refinance without a degree • Offers up to 36 months of academic deferment |
• Only available to students that are residents of or attended school in Indiana • No biweekly payment via autopay • You can’t refinance parent PLUS loans in your name • Cosigner release option after 48 months of timely payments |
ISL Education Lending is a nonprofit student lender offering both private student loans and student loan refinancing. ISL Education Lending is best for borrowers who want to work with a nonprofit lender, want competitive interest rates, or want to refinance without having a degree.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Competitive interest rates and zero fees • You can refinance without a degree • Cosigner release option after 24 months |
• Only one loan repayment term for in-school refinancing • Students cannot take over parent PLUS loans that parents took out on their behalf • No biweekly payment via autopay |
LendKey’s student loan refinancing is a good option if you have graduated, have a strong credit score, and have stable income. A great feature of LendKey is that they will connect you with a network of 100+ lesser known credit unions and community banks so you can work with and take out loans from smaller institutions. LendKey is best if you are a creditworthy borrower and want to work with smaller lenders with low rates and good customer service.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Work with a credit union or community bank, rather than a traditional lender • Access to competitive interest rates • Offers up to 18 months of forbearance • Free borrower benefits like Career Assistance, Credit Health Analysis, and Federal Student Loan Assistance |
• Eligibility criteria excludes part-time students, parents, and non-U.S. citizens/permanent residents • Varying cosigner release policies • Loans aren’t available in Maine, Nevada, North Dakota, Rhode Island, or West Virginia • Biweekly payment via autopay is not available • You may have to become a member of a credit union |
Nelnet Bank offers student loan refinancing for both private and federal student loans, including parent PLUS loans. Nelnet Bank also offers a flexible forbearance policy and competitive interest rates. Nelnet Bank is best if you are looking for competitive rates and want the ability to refinance student loans, including parent PLUS loans.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Competitive interest rates • You can refinance parent PLUS loans in your name • Offers 12 months of forbearance due to economic hardship or natural disaster • Cosigner release option after 24 months of timely payments • Flexible repayment options |
• Strict eligibility criteria • No biweekly payment via autopay • Not accessible to international students or borrowers with student visas |
SoFi is one of the biggest student loan refinancing companies in the industry. You have to have an associate’s degree or higher to qualify, but if you do qualify, you’ll have access to a wide variety of repayment options and exclusive member benefits. SoFi is best if you have at least an associate’s degree, are a creditworthy borrower, and want to take advantage of their benefits.
| Best Features | Drawbacks |
| • Competitive interest rates • Students can refinance parent PLUS loans in their own name • Comes with borrower protections (forbearance and deferment) |
• Unclear about credit requirements • No cosigner release • Refinancing is unavailable to borrowers without a degree • No spousal consolidation loans |
Final Thoughts from the Nest
While there are a variety of factors that make a lender or refinance loan good, the best loan will always be the one that works best for you. To discover the best refinancing companies and which option is best for you, complete the Sparrow application.
In just a few minutes, we’ll show you what refinance loans you qualify for with 15+ top lenders. Then, we’ll help guide you through the process of selecting the best refinance loan so you can be confident in your lending decision.
Sparrow’s goal is to give you the tools and confidence you need to improve your finances. Many or all of the products featured here are from our partners who compensate us. This may influence which products we write about and where and how the product appears on a page. However, this does not influence our evaluations. Our opinions are our own. While we make an effort to include the best deals available to the general public, we make no warranty that such information represents all available products.